What Are DUI/DWI Charges and Offenses?
Among the most common criminal cases in the United States are DUI/DWI charges and offenses, yet they carry some of the most severe and lasting consequences. Whether it’s your first time or a repeat violation, understanding the details of these offenses is essential to protect your legal rights and driving privileges.
Driving under the influence (DUI) or driving while intoxicated (DWI) charges typically stem from being caught operating a vehicle with a blood alcohol concentration (BAC) over the legal limit or while impaired by drugs. These charges can range from misdemeanors to felonies depending on several factors, including your BAC, prior offenses, and whether anyone was harmed.
Common Types of DUI/DWI Charges Across the U.S.
The criminal justice system classifies DUI/DWI offenses based on severity, intent, and the driver’s history. Here are the most common categories:
First-Time Offenses vs. Repeat Offenses
A first-time DUI is often charged as a misdemeanor. Penalties typically include license suspension, fines, mandatory alcohol education, and sometimes a brief jail sentence. However, even a first offense can significantly affect your life, especially in terms of employment, insurance rates, and your criminal record.
Repeat DUI/DWI offenders face harsher penalties. A second or third DUI can lead to longer license suspension, installation of an ignition interlock device, and mandatory substance abuse programs. In many states, a third offense is treated as a felony.
If you’re unsure how repeat offenses are treated in your state, it’s crucial to learn about DUI laws and how they impact your specific case.
Underage DUI Charges
Most states enforce a zero-tolerance policy for drivers under 21. That means any measurable BAC can lead to arrest and charges. In these cases, even a single beer could result in license suspension, fines, and a permanent record that can affect college admissions and job applications.
Aggravated DUI/DWI Offenses
Certain conditions can elevate a standard DUI to an aggravated charge. These may include:
- Extremely high BAC levels
- Causing injury or death
- Driving with a suspended license
- Having a child passenger
- Fleeing the scene of an accident
Aggravated DUI/DWI charges come with more severe penalties, including long-term license revocation and mandatory prison time in some jurisdictions.
Legal Penalties for DUI/DWI Offenses
Whether you’re facing a misdemeanor or felony, the consequences of a DUI/DWI conviction can follow you for years. Most states enforce a range of penalties, some of which are mandatory.
Jail Time, Fines, and License Suspension
Penalties vary widely, but typical outcomes include:
- Fines: First-time offenders may face court costs and fines that vary by state and offense level.
- Jail Time: Some states impose mandatory jail sentences even for first offenses, while others offer alternatives like community service or probation.
- License Suspension: A DUI conviction almost always results in temporary loss of driving privileges, with durations increasing for each subsequent offense.
License reinstatement often requires satisfying several conditions, including payment of fees, attendance at DUI classes, and proof of SR-22 insurance—a specialized form of high-risk auto insurance. You can explore SR-22 insurance requirements to understand what this entails in your state.
Ignition Interlock Devices and Mandatory Programs
In many states, ignition interlock devices (IIDs) are now a standard penalty for DUI/DWI convictions. These breathalyzer-type devices are installed in your vehicle and require a clean BAC sample before starting the car.
IIDs are often mandated even for first offenses, depending on the BAC level or the presence of minors in the vehicle. They must be maintained at your expense and monitored by a state-approved vendor. If ordered to install one, it’s important to understand ignition interlock requirements and stay compliant.
Additionally, courts may require alcohol education classes, treatment programs, or attendance at DUI victim impact panels. These conditions are often part of probation agreements or license reinstatement requirements.
How DUI/DWI Laws Differ by State
DUI/DWI charges & offenses are handled differently across the United States, which can significantly affect the outcome of a case depending on where it occurs. While the general legal limit for blood alcohol concentration (BAC) is 0.08%, the penalties and procedures beyond that point differ widely by jurisdiction.
Overview of Penalty Variations in Key States
- Texas: Mandatory minimum jail time for repeat offenders and stricter penalties for high BAC or child passengers.
- California: Requires installation of an ignition interlock device for most offenders and includes license suspension even before conviction via administrative procedures.
- New York: Implements “Leandra’s Law,” making it a felony to drive intoxicated with a minor in the vehicle.
- Arizona: Known for having some of the strictest DUI laws in the country, including mandatory jail time and treatment for first offenders.
- Florida: Utilizes tiered penalties depending on BAC and whether injuries occurred, with first offenders often required to attend DUI school.
If you’re unsure what laws apply to your case, it’s best to learn about DUI laws in your state. Some states may also differentiate between DUI (alcohol) and DWI (drugs or other impairing substances).
DWI vs. DUI: Terminology and Legal Differences
Some states use “DUI” (Driving Under the Influence), others use “DWI” (Driving While Intoxicated), and a few use both. The terminology may also reflect the substance involved:
- DUI often refers to alcohol or drugs
- DWI may indicate a higher level of impairment or apply only to alcohol in certain jurisdictions
For example, in Texas, both DUI and DWI exist, with DUI often used for minors and DWI for adults. In North Carolina, DWI is the only recognized term, and penalties can escalate quickly based on prior offenses.
What Happens After a DUI/DWI Arrest?
Understanding the post-arrest process can help reduce anxiety and improve your ability to respond strategically. The legal timeline moves fast, and missing a key step can hurt your chances of a fair outcome.
From Arrest to Arraignment: The Legal Process
- Traffic Stop or Checkpoint: You may be pulled over for erratic driving or stopped at a sobriety checkpoint. Officers may request field sobriety tests or a breathalyzer.
- Arrest: If you fail the test or refuse it, you’ll likely be arrested and taken into custody.
- Booking: Personal information is collected, fingerprints taken, and charges are formally entered.
- Administrative License Suspension (ALS): In many states, your license may be automatically suspended before your court date.
- Arraignment: This first court appearance allows you to enter a plea. It’s often your first opportunity to have legal representation.
It’s important to understand your rights and obligations during this process. If you’re facing an upcoming arraignment or license suspension, consider reaching out to find a DUI attorney who can help guide your defense from the start.
License Suspension and SR-22 Insurance
Once a DUI/DWI charge is filed, many states impose an administrative license suspension, separate from the court system. Even if you are ultimately found not guilty, the DMV may still restrict your driving privileges unless you appeal the suspension.
To regain your license, you’ll typically need:
- Proof of insurance (SR-22 certificate)
- Completion of a DUI program
- Payment of reinstatement fees
You can explore SR-22 insurance requirements to learn what this process involves in your state.
How Legal Help Can Change the Outcome
Facing DUI/DWI charges & offenses without legal guidance is risky. Every decision you make—from what to say during a traffic stop to how you plead in court—can impact your future.
DUI Attorneys and Defense Strategies
A qualified DUI defense lawyer can:
- Evaluate whether the traffic stop was lawful
- Challenge breathalyzer or field sobriety test results
- Negotiate plea deals to reduce or dismiss charges
- Advocate for your eligibility for diversion or rehab programs
If you don’t know where to begin, take the first step to explore your legal options and connect with experienced legal professionals who specialize in DUI cases.
DUI/DWI Diversion Programs and Classes
Some states offer diversion programs for first-time or low-risk offenders. These programs may include:
- Alcohol education or treatment
- Victim impact panels
- Community service
- Regular monitoring
Successful completion can lead to reduced charges or case dismissal. To get started, you can look into available DUI/DWI classes or speak to a lawyer about whether you qualify.
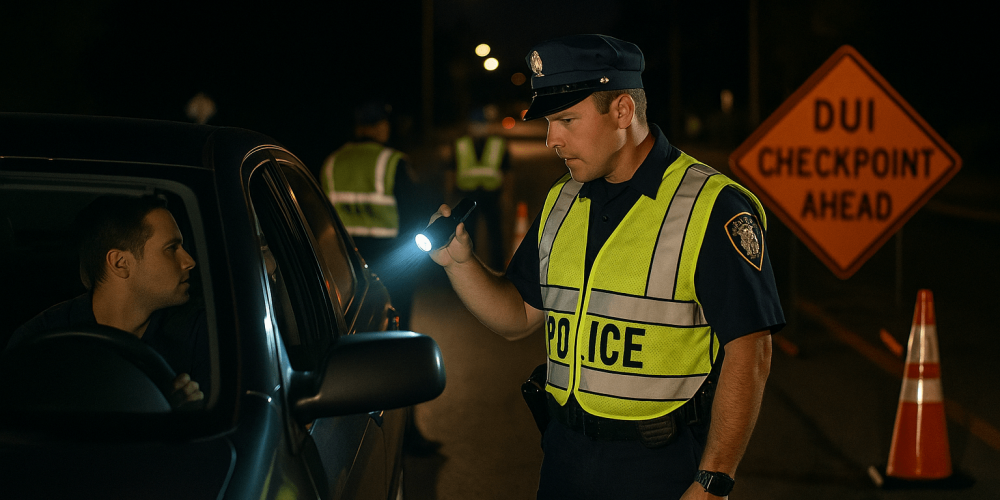
How DUI Checkpoints and Field Sobriety Tests Affect Charges
One of the most common ways people encounter DUI enforcement is through sobriety checkpoints or routine traffic stops. These encounters often serve as the starting point for DUI/DWI charges & offenses, and understanding your rights and obligations during these stops can significantly affect your case outcome.
DUI Checkpoints: Are They Legal?
DUI checkpoints, also known as sobriety checkpoints, are legal in many states and serve as a proactive method for law enforcement to detect impaired drivers. Officers briefly stop vehicles and may request that drivers submit to:
- Visual inspection
- Field sobriety testing
- Preliminary breath testing
While these checkpoints must follow strict guidelines to be constitutional, refusal to cooperate can still lead to arrest in most states. If you’re concerned about how checkpoints are handled in your area, it’s helpful to learn about DUI checkpoints and your rights under local law.
Field Sobriety and Breathalyzer Tests
If an officer suspects impairment, they may conduct field sobriety tests such as:
- The horizontal gaze nystagmus (HGN) test
- The walk-and-turn test
- The one-leg stand test
Failing any of these can establish probable cause for arrest, even before chemical testing is conducted. Many people don’t realize they can politely decline field sobriety tests in some states without immediate penalties, although chemical test refusals (like a breathalyzer) usually result in automatic license suspension.
You can better prepare by reviewing DUI/DWI resources that explain what to expect and how to respond at checkpoints or during traffic stops.
Know Your Rights in DUI/DWI Cases
Facing DUI/DWI charges & offenses is stressful, but you don’t have to navigate the legal system alone. These charges carry real consequences—both immediate and long-term. From jail time and fines to ignition interlock mandates and SR-22 insurance, the repercussions can follow you for years.
That’s why understanding your state’s laws, the criminal process, and available legal defenses is essential. First-time offenders may be eligible for diversion programs or reduced penalties, while repeat offenders need a more aggressive legal strategy. In either case, the support of a DUI defense attorney can help you avoid the worst outcomes.
If you’ve recently been arrested or charged, don’t wait to act. Being proactive could mean the difference between a conviction and a second chance.
Explore Legal Help for DUI/DWI Charges Today
Legal help is one of the most effective tools for managing DUI/DWI charges & offenses. Whether you’re dealing with a first offense or a felony-level case, a qualified attorney can evaluate your situation and recommend the best course of action.
Take the next step to:
- Get a free consultation and understand your rights
- Find a DUI attorney in your local area
- Explore your legal options through professionals who specialize in DUI defense
- Learn about DUI laws that apply to your jurisdiction
The sooner you seek guidance, the more informed you can be about your legal options and next steps.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What’s the difference between DUI and DWI?
The terms are often used interchangeably, but they can differ by state. DUI usually refers to “Driving Under the Influence,” while DWI stands for “Driving While Intoxicated.” Some states assign different penalties depending on the substance involved or the level of impairment.
2. How long do DUI charges stay on your record?
A DUI conviction can stay on your criminal and driving record for years, sometimes permanently. Some states allow expungement after a waiting period, especially for first-time offenses with no aggravating circumstances.
3. Can a DUI be reduced or dismissed?
Yes, in some cases. A skilled attorney may negotiate for a reduced charge, like reckless driving, or identify procedural issues (such as faulty breath tests) that could lead to dismissal.
4. What happens if you refuse a breathalyzer test?
Refusal can lead to automatic license suspension, even if you’re not convicted of DUI. In many states, this is part of the “implied consent” law you agree to when you get a driver’s license.
5. Do DUI penalties increase for a second offense?
Absolutely. A second DUI usually carries harsher penalties, including longer license suspension, higher fines, mandatory jail time, and possibly felony classification depending on the state.
Key Takeaways
- DUI/DWI charges & offenses vary widely by state and case severity
- First-time offenders often face fines, license suspension, and DUI education
- Repeat or aggravated offenses may lead to felony charges and jail time
- Legal guidance can help reduce penalties or dismiss charges entirely
- Proactive steps, like getting a free consultation, can protect your rights and future